Table of Contents
.png)
When working with gas welding equipment like MIG or TIG welders, it's essential to have a solid understanding of gas cylinders, as they are critical to safety and efficiency. Gas cylinders are highly pressurised vessels used to store gases used in welding, and handling them correctly is crucial due to the inherent risks of high-pressure gases.
This blog post will cover the advantages of ownership vs. rental gas cylinders, including the basics of gas cylinders, types of gases they might contain and their uses in welding. We'll discuss safety standards and practices vital for safely handling these cylinders. Additionally, we'll look at the importance of proper storage to prevent accidents and ensure a safe working environment.
Ownership vs Renting
Whether to own or rent a gas cylinder depends mainly on the frequency of use and financial considerations. Owning a cylinder means taking on the responsibility for its maintenance and compliance with safety standards. This is cost-effective in the long run for those who use gases infrequently as there is no monthly fee to pay.
Renting a cylinder, on the other hand, shifts the burden of maintenance and testing to the gas provider. This is typically accompanied by a cylinder refill fee each time a full cylinder is collected and a monthly rental fee. For frequent users, renting can be more convenient and ensure that cylinders meet the latest safety standards.
Another option is Coregas Trade N Go gas cylinders, a convenient alternative to owning or renting gas cylinders. Instead of committing to a long-term rental or purchasing your cylinders, Trade N Go allows you to pay for the gas refills each time a full cylinder is collected, with a minimal initial bond, which can be refunded when the cylinder is returned and no longer required. This system is ideal for those who need gas irregularly or want to avoid the upkeep and storage responsibilities of owning cylinders. It's a straightforward pay-as-you-go service that ensures you always have access to the gas you need without the long-term commitment or upfront costs. For more detailed information, you can visit the Coregas page here.
Ownership Advantages:
Long-Term Cost Savings: Ownership eliminates recurring rental fees, making it more cost-effective for regular users over time.
Convenience: Users pay only for the gas they need when needed, avoiding the costs associated with cylinder rental fees.
Unrestricted Access: Immediate and constant access to cylinders is crucial for continuous gas supply operations.
Full Control: Owners manage their maintenance and compliance, ensuring cylinders meet exact safety standards without dependency on a third party.
Investment in Assets: Cylinders become company assets, potentially enhancing the value of business resources.
Rental Advantages:
Hassle-Free Maintenance: The rental company handles all maintenance, testing, and certification, reducing the administrative burden.
Flexibility: Allows for easy swapping or upgrading of cylinders as needs change without the need to sell or dispose of owned assets.
Updated Technology: Ensures access to the latest cylinder technologies and safety features as rental companies keep their inventory current.
Trade N Go Advantages:
Low Upfront Cost: The minimal initial bond is refundable upon return, making it ideal for those with sporadic needs.
Convenience: Users pay only for the gas they need when needed, avoiding the costs associated with cylinder upkeep and storage.
Simplicity: A straightforward system that eliminates the complexities of cylinder ownership and long-term rental agreements.
Immediate Availability: Provides quick access to gas without the long-term commitment, perfect for occasional users.
Gas Cylinder Options from Proline Industrial
For those heavily involved in MIG welding, Proline Industrial offers a cost-effective solution that reduces operational costs and boosts welding efficiency—the ownership of a 5kg CO2 gas cylinder.
Owning your CO2 cylinder eliminates ongoing rental charges and provides about 10 hours of MIG welding time based on an 8/10 L/minute flow rate.
CO2 is the most common reactive gas used in MIG welding and can be used in its pure form without adding an inert gas. This makes CO2 an inexpensive option and an attractive choice for reducing material and operational costs. CO2 also provides deeper weld penetration and a slightly narrower bead, which is advantageous for welding dirty, coated, or rusty materials.
In addition to CO2, Proline Industrial offers a range of other gases tailored to meet various welding and cutting needs. Argon is a popular choice for TIG welding and MIG welding of non-ferrous metals, such as aluminum and magnesium, due to its excellent arc stability and low reactivity, which helps produce clean and precise welds.
Acetylene, combined with oxygen, is essential for oxy-acetylene welding and cutting, providing a high flame temperature that allows for efficient and effective cutting of ferrous and non-ferrous metals.
Oxygen is also available for enhancing combustion in cutting and welding processes, ensuring clean and strong welds. Additionally, oxygen is used in plasma cutting and other cutting techniques where a focused heat source is needed to achieve fine cuts and edges. In welding, oxygen is often used to increase the heat of the flame, enabling faster and more efficient metal joining. Overall, oxygen gas is indispensable in the metalworking industry for its ability to enhance the performance and quality of welding and cutting operations.
Additionally, Coregas09, a specific CO2 and Argon gas mixture designed for welding carbon steel, as it provides a stable arc, reduced spatter, and excellent weld bead appearance. The presence of argon in the mix ensures a smooth arc and reduces oxidation, while CO2 contributes to deeper penetration and increased weld strength. This combination makes CO2-Argon mixed gas ideal for achieving high-quality welds in a variety of applications, including automotive manufacturing, construction, and general fabrication.
Proline Industrial’s diverse gas options ensure that professionals can select the most suitable gases for their specific requirements, enhancing both productivity and quality, view all options here.
Pressure and Testing Requirements
Gas cylinders are categorised as pressure vessels and are subject to stringent testing to meet safety standards. The frequency of these tests varies by gas type—typically every ten years, but every five years for CO2 cylinders, reflecting the different stability and reactivity of the gases. Only certified testers can carry out these tests; similarly, only certified fillers can legally refill cylinders. It’s crucial to ensure that your gas cylinders are always within their valid test period and have a clear, legible test stamp.
Colour Coding for Safety and Identification
Cylinders are colour-coded according to the gas they contain for safety and ease of identification. This colour coding is essential for user convenience and for preventing accidents that could arise from misidentification. For instance, oxygen cylinders are black, acetylene cylinders are maroon, and argon cylinders are blue. Adhering to these colour standards is not just a matter of compliance but a critical safety practice.
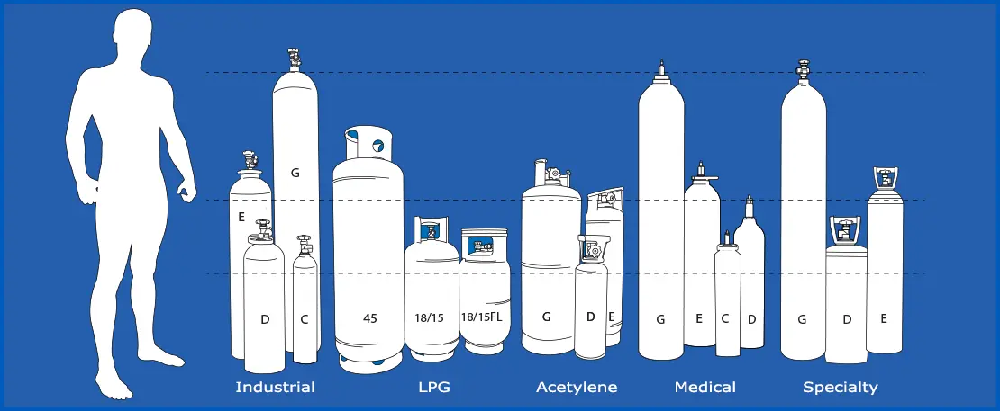
Cylinder Sizes and the Importance of Correct Gas Matching
Gas cylinders come in various sizes to accommodate different gas volumes, typically ranging from 0.5 cubic meters to 10.5 cubic meters. It's crucial to ensure that each type of gas is stored in the correct cylinder, as using the wrong one can lead to dangerous cross-contamination. Gas companies enforce strict guidelines to minimise risks, including using colour-coded and regularly tested cylinders. This helps prevent accidents by ensuring that each gas is only stored in cylinders suited to its properties and safety requirements.
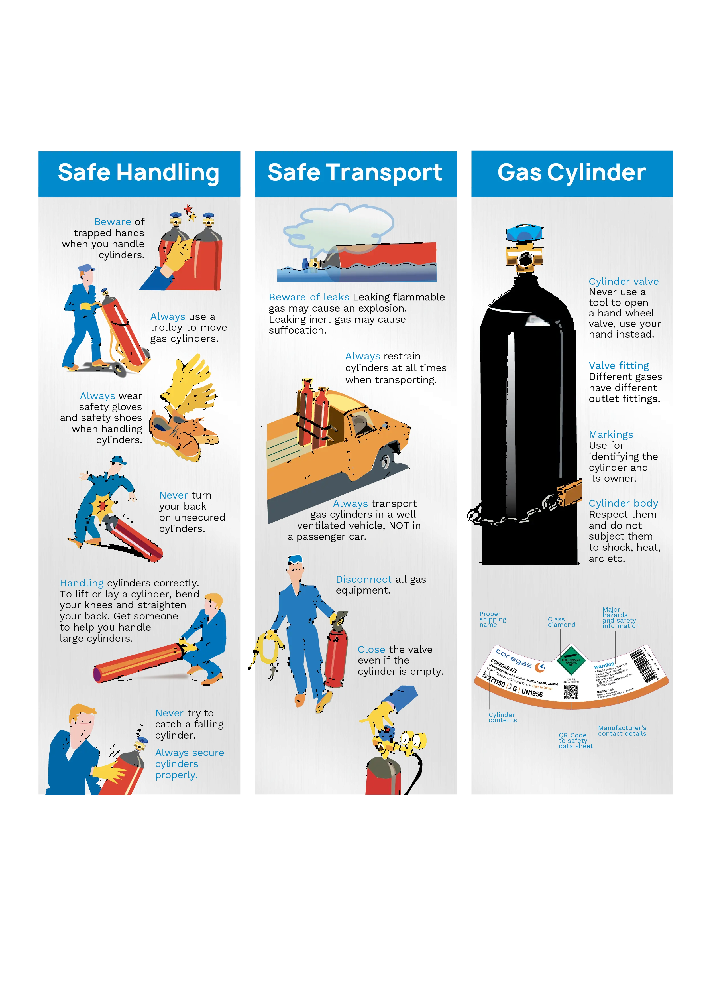
Safety Measures and Legal Requirements
Handling gas cylinders requires adherence to legal standards and safety protocols.
Compliance with legal and safety standards is about avoiding penalties and ensuring a safe working environment. The use of certified professionals for testing and refilling highlights the importance of adhering to regulations designed to prevent accidents and ensure the secure handling of potentially dangerous gases.
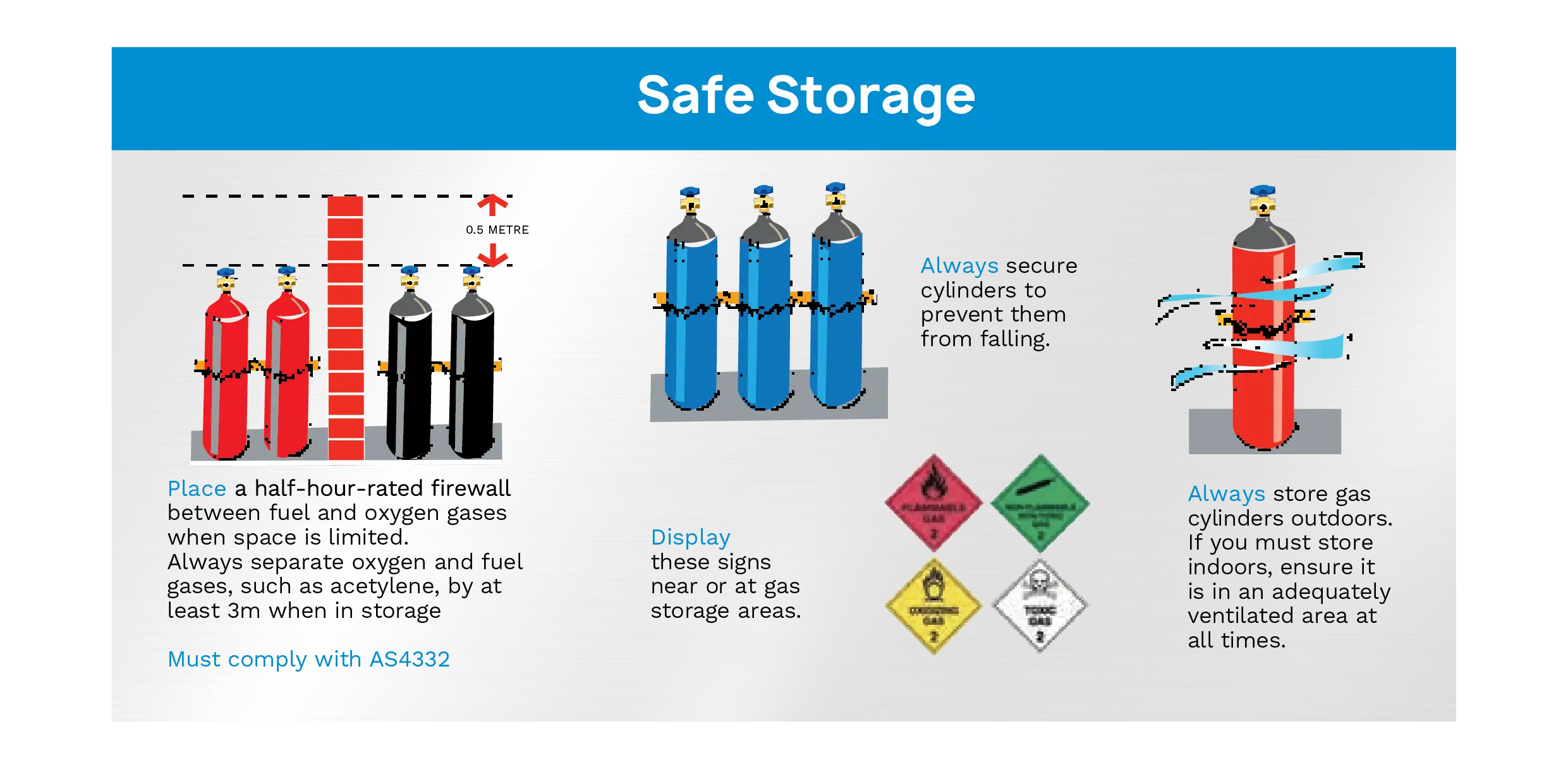
Filling gas cylinders that are out of their valid test period or lack a test stamp is illegal and highly hazardous. This regulation ensures that only cylinders in optimal condition are in use, thus mitigating risks like leaks or explosions. Regular testing and certification by qualified professionals are not just legal requirements—they are critical safety measures that protect users and their environments.
Misuse and improper storage of gas cylinders can have dire consequences. Modifying cylinder colours or using gas cylinders for unintended purposes can lead to accidents or inefficient operation. Proper storage away from heat sources, in a cool, ventilated area, and an upright position is essential for maintaining cylinder integrity and safety.
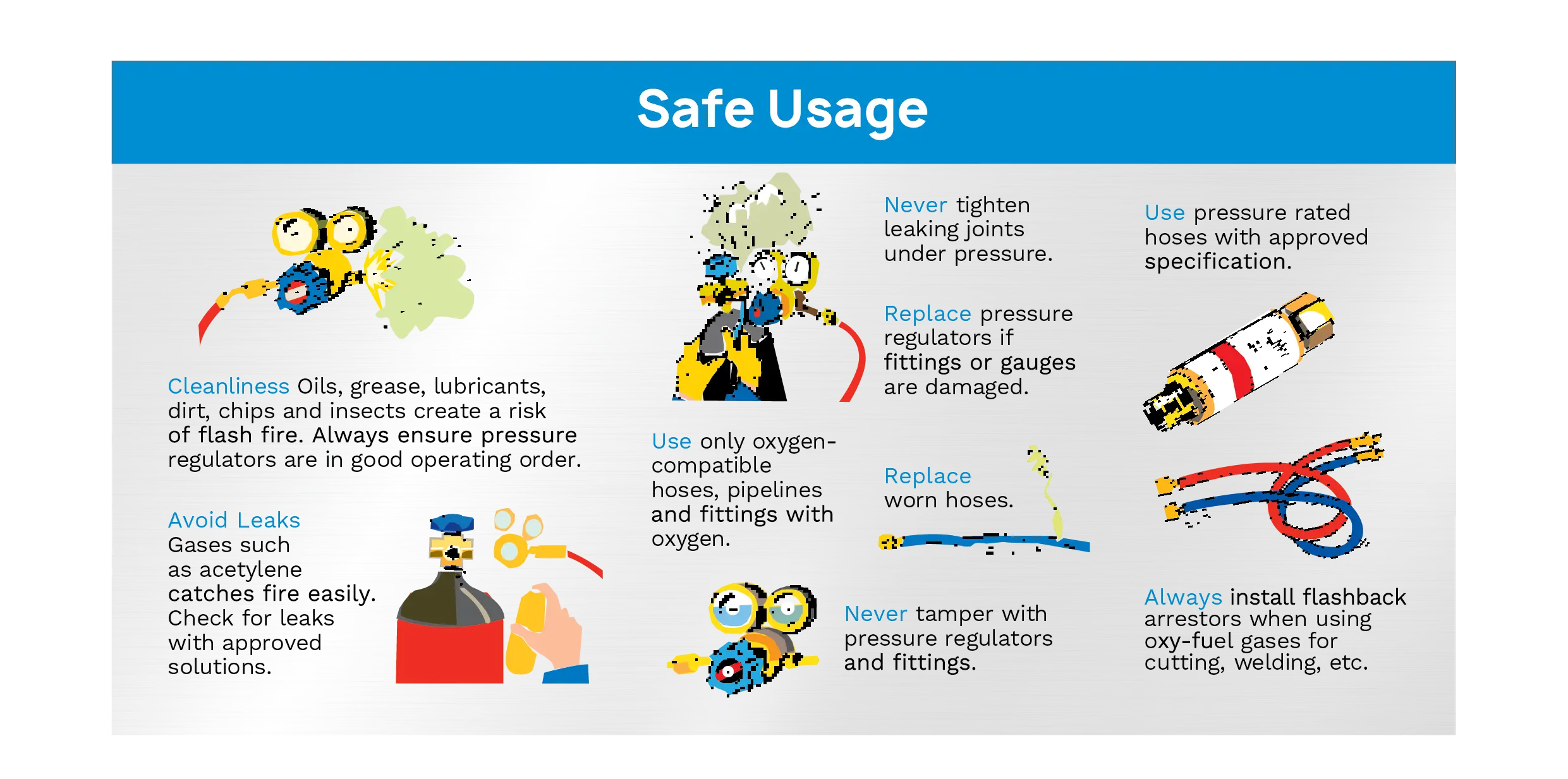
Failure to adhere to legal standards can result in fines, legal action, and severe safety incidents. The regulations governing gas cylinders are stringent because the stakes—personal injury, property damage, and environmental harm—are exceptionally high. Compliance is not optional but essential for legal operation and personal safety.
Practical Tips for Gas Cylinder Management
Several practical tips must be considered to ensure safety and efficiency in managing gas cylinders effectively. Whether you own or rent, the following guidelines will help you maintain your cylinders in top condition.
1. Choosing the Right Cylinders for Different Gases
Selecting the appropriate cylinder for the specific gas you need is the first step in cylinder management. Each gas has its requirements regarding pressure and cylinder material compatibility. For example, acetylene must be stored in cylinders containing a porous material soaked with acetone to stabilise the gas under pressure.
2. Maintenance Tips to Prolong Cylinder Life
Regular inspections for damage, adherence to refill schedules, and proper handling can significantly extend the life of a gas cylinder. Avoid exposing cylinders to extreme temperatures or physical shocks, which can compromise their integrity. Also, ensure that the storage area complies with all safety regulations, such as those specified by the Hazardous Substances and New Organisms (HSNO) regulations.
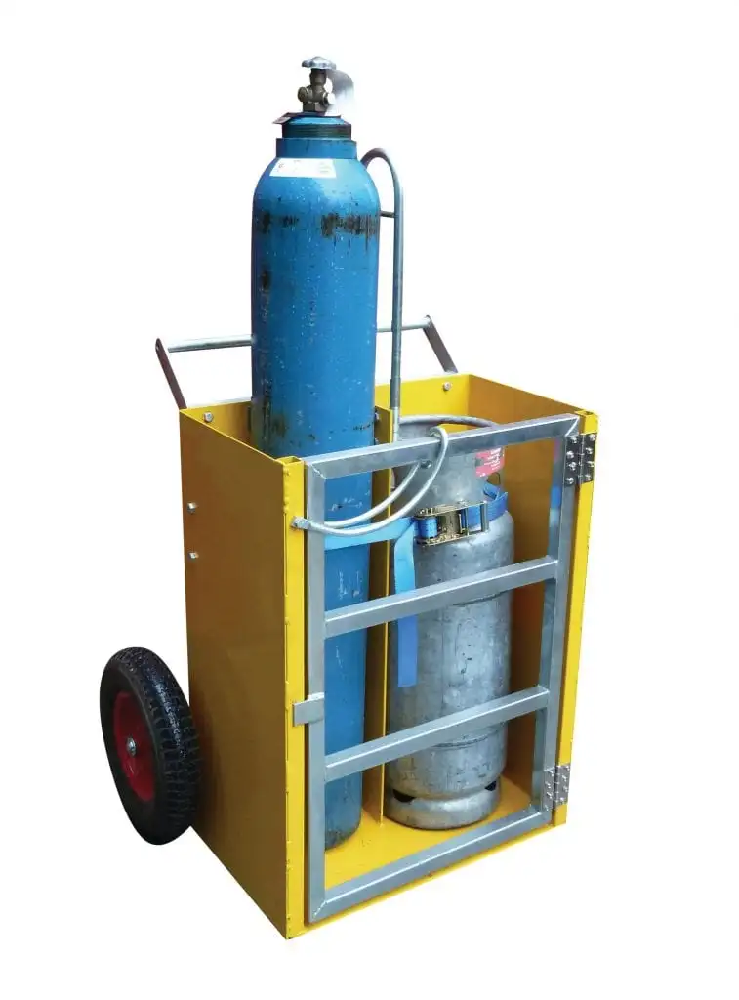
3. Safety Protocols for Cylinder Storage and Handling
Always store cylinders upright and secure them to prevent tipping. Use chains or adequate stands designed for cylinder storage. Ensure the storage area is well-ventilated and away from potential ignition sources. Regular checks for leaks and using soapy water on the valves and connections can prevent accidents before they occur.
In conclusion, gas cylinders are indispensable tools in welding and other industrial applications, but their use comes with significant responsibilities. Understanding the technical specifications, adhering to legal standards, and implementing rigorous safety practices are essential for these high-pressure cylinders’ safe and effective use. Whether you own or rent your cylinders, maintaining and using them correctly should be your top priority. For more detailed information on the various types of gas cylinders, whether you're considering owning, renting, or using a Trade N Go system, you can contact our team at Proline Industrial.

















































